Permutation Formula
The permutation formula calculates the possible permutations of elements out of a group of elements where order matters. See the combination formula for where order does not matter.
Formula Terms
| Expression | Description |
|---|---|
| The total number of elements in the group | |
| The number of elements to select | |
| Factorial operator |
The permutation formula calculates the possible permutations of elements out of a group of elements where order does matter. For example, the possible permutations of choosing elements from elements is given by the expression below.
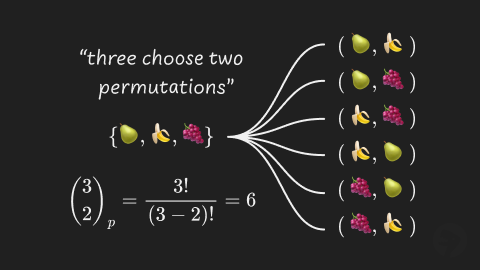
There are possible permutations of choosing elements from elements. We can visualize this example using the three fruits {🍐, 🍌, 🍇}. The possible permutations of “three choose two” are shown below.
- (🍐, 🍌)
- (🍐, 🍇)
- (🍌, 🍇)
- (🍌, 🍐)
- (🍇, 🍐)
- (🍇, 🍌)
To calculate the possible permutations of choosing two items from the set {♣️,♦️,♥️,♠️}, substitute into the equation for the size of the set and into the equation for the number of items we are choosing.
Expand the factorial operator and simplify.
There are possible permutations of choosing two items from the set {♣️,♦️,♥️,♠️}. This is twice the number of combinations because each combination can be arranged in different orders. The possible permutations of “four choose two” are shown below.
- (♣️, ♦️)
- (♣️, ♥️)
- (♣️, ♠️)
- (♦️, ♥️)
- (♦️, ♠️)
- (♥️, ♠️)
- (♦️, ♣️)
- (♥️, ♣️)
- (♠️, ♣️)
- (♥️, ♦️)
- (♠️, ♦️)
- (♠️, ♥️)
The combination formula calculates the possible combinations of r elements out of a group of n elements where order does not matter.
The number of permutations of n distinct items is given by n factorial. A permutation is a unique ordering or arrangement of the set of items.