The constant (tau) is a geometric constant defined as the circumference of a circle divided by its radius.
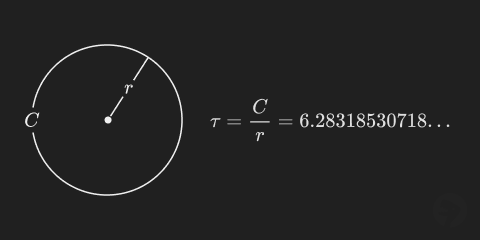
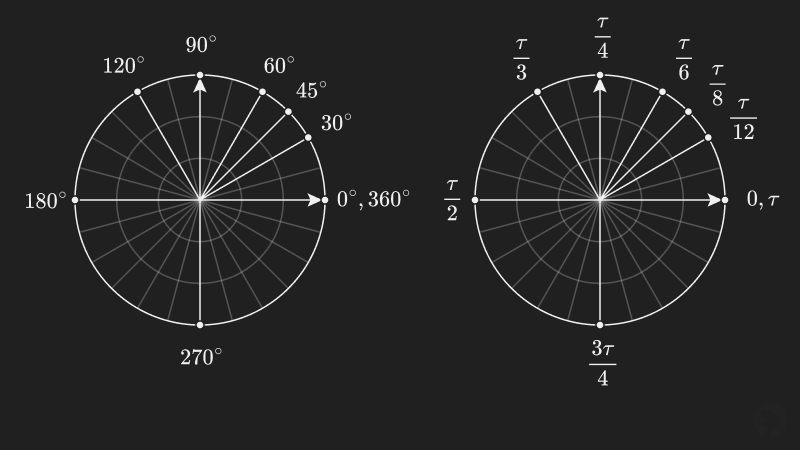
The constant can be used as an alternative to (pi) where in equations, formulas, and the radian angle system. For example, shown below are some common angles measured in degrees and radians using .
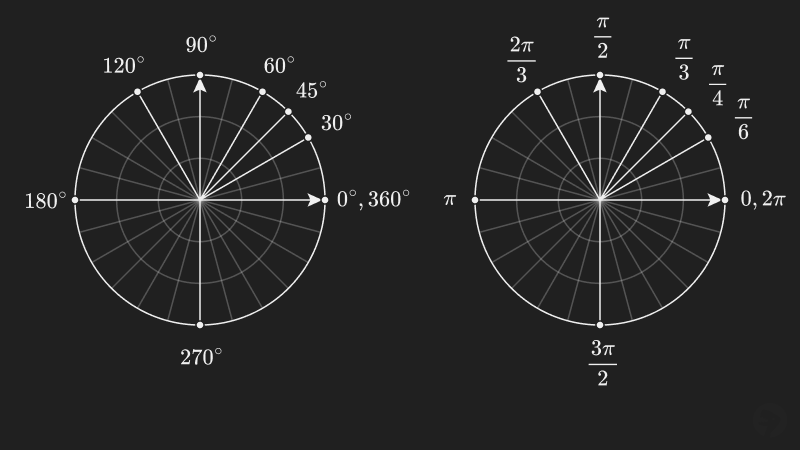
There is some discussion whether should be used instead of in equations and formulas[1]. For comparison, shown below are some common angles measured in degrees and radians using .
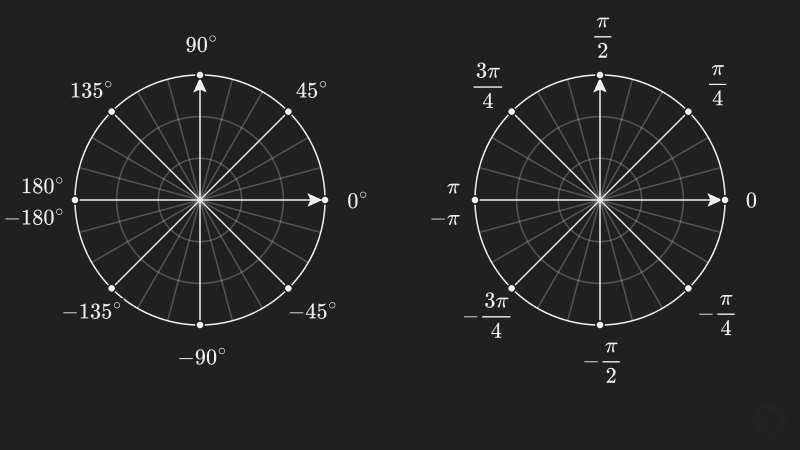
When measuring angles in radians using , like when graphing trigonometric functions, the full range of rotation is usually represented as to radians as shown below.
The Greek letter π (pi) is a geometric constant approximately equal to 3.1416. Its value is equal to the length of any circle's circumference divided by its diameter.
The radian angle system is a unit of measure for angles. To measure an angle in radians, divide the arc length of the angle by the radius used to draw the arc. A full rotation is equal to 2π radians.
-
No, really, pi is wrong: The Tau ManifestoMichael Hartl