The symbol (pi) is used in math as a geometric constant in formulas and the radian angle system. The value of is defined as the length of any circle’s circumference divided by its diameter.
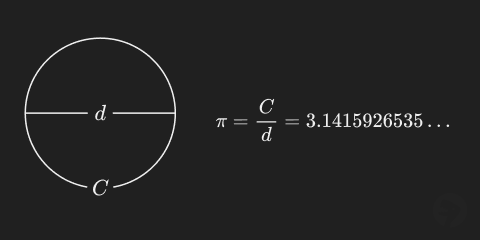
The value of is irrational, meaning that it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. For most calculations involving , a surprisingly small number of decimal places (less than 100) are needed to achieve the desired accuracy. See this page for the first 100 decimal places of .
Shown below are some formulas where inline (pi) is used.
Calculate the area of a circle given the radius.
Calculate the circumference of a circle given the radius.
Calculate the volume of a sphere given the radius.
Calculate the volume of a cylinder given the radius and height.
The constant (pi) is used when measuring angles in radians to represent a half rotation. Shown below is the radian angle system labeled using on the left and on the right.
The circle constant τ (tau) is a geometric constant approximately equal to 6.283. The numeric value is defined as the length of any circle's circumference divided by the length of its radius.
The radian angle system is a unit of measure for angles. To measure an angle in radians, divide the arc length of the angle by the radius used to draw the arc. A full rotation is equal to 2π radians.