The inscribed angle theorem states that for any three points on a circle, an inscribed angle is equal to one-half the central angle that subtends the same arc.
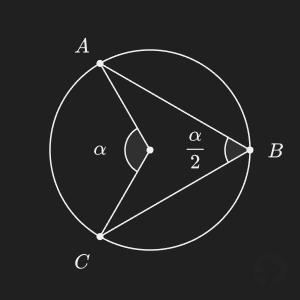
There is an interesting special case of the inscribed angle theorem where the inscribed angle is a right angle.
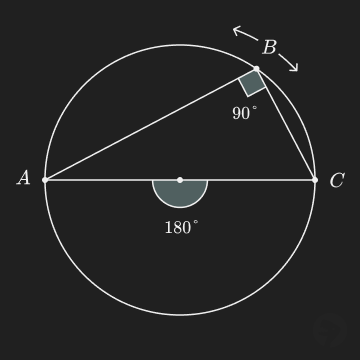
This case occurs when the central angle is degrees, which forms a straight line . Then, for any point on the circle, the inscribed angle is equal to degrees. This fact can be used to derive the double angle formula for sine and cosine.
Ptolemy's Theorem states that for a quadrilateral inscribed on a circle, the product of the lengths of the diagonals equals the sum of the products of the lengths of pairs of opposite sides.